
Economic Growth
The increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of goods and services
It can be defined as " the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy over time; usually, a year, measured as the percentage increase in the real gross domestic product (GDP)."

Usually, increases in aggregate production correlate with increased marginal productivity by each resident, leading to increased average incomes, greater consumer spending, and an improved standard and quality of living.
The rate of economic growth refers to "the geometric annual rate of growth in GDP between the first and the last year over a while, that represents the trends in the average level of GDP."
An increase in economic growth can be either intensive or extensive. Intensive growth refers to an increase caused by more efficient use of inputs, whereas extensive growth refers to an increase caused by increases in the number of inputs.
Economic growth mostly differs from economic development.
Economic development is seen as being restricted to economies close to the subsistence level, whereas economic growth is applied to economies experiencing rising incomes and more buying power.
The Industrial Revolution is a significant example dealing with the enhancement of the variables used for production, which contributed to economic growth.
The variables and factors are human capital, technology, capital goods, and the overall size of the workforce.
Automated assembly in factories shifted workers into more skilled and specialized roles, thereby increasing technology. Together they led to increasing the availability of capital goods due to more production and the end of periodic famines.
Factors affecting economic growth
1. Human Resources
It is an essential determinant as the quality and quantity of human resources available in an economy can directly affect the growth of that specific economy.
The term quality of human resources indicates skills, training, education, and creative abilities. A highly skilled and trained human resource would give an output of high quality.

With quantity, it is seen that a shortage of skilled labor affects the growth of an economy. This means that it is essential to have adequate amounts of human resources to achieve economic growth, prosperity, and resilience.
2. Natural Resources
It is an important factor that depends on the climate and environmental conditions. Natural resources refer to the resources that are either produced on the land or beneath the land by nature.
The land resources include water resources, plants, and landscapes, and beneath the land, resources include oil, metals, non-metals, natural gas, and minerals.

Apart from plenty of availability, the efficient utilization of natural resources is essential for economic growth, which is achieved with the help of skills and abilities of human resources, technologies used, and the availability of funds.
3. Capital formation
Producing and acquiring man-made products like buildings, power, machinery, a medium of communication, and transportation is termed capital formation.
Capital formation leads to an increase in capital/labor ratio by increasing the availability of capital per worker, which in turn increases labor productivity and ultimately increases the output and growth of the economy.
4. Technological development
This involves the application of scientific methods and production techniques and can be defined as technical instruments used by a certain amount of labor in an economy.
Technological improvement facilitates increased productivity with the limited availability of resources. The economies that move hand in hand with technological development grow rapidly compared to other economies.

Also, it is necessary to choose the right technology as this selection plays an essential role in affecting the growth of an economy. The correct choice of technology leads to an increase in the efficiency of production.
5. Social and political factors
Traditions, customs, values, and beliefs come under the banner of social factors that contribute to the growth of an economy.
Along with social factors, political factors like the participation of the government in the formulation and implementation of various policies have a major impact on economic growth.
The factors affecting economic growth can be seen as demand-side factors and supply-side factors:
| s.no | Demand AD = C+I+G+X-M | Supply-side(long-run aggregate supply) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Higher real wages ↑C | Increased investment |
| 2. | Tax cut ↑C | Higher labor productivity |
| 3. | Devaluation ↑X ↓M | Discover raw materials |
| 4. | Government spending ↑G | Increase in labor force |
| 5. | Lower interest rate ↑I ↑C | Improved technology |
Demand-side says that any increase in consumption, investment, government spending, or exports will lead to higher aggregate demand and economic growth.
In the long run, no increase in long-run aggregate supply makes a rise in an AD an inflationary move.
Theories of economic growth
1. Adam Smith
The basic approach of his idea deals with competitive behavior and equilibrium dynamics, the need for diminishing returns, and its role in physical and human capital accumulation.
His idea also deals with the interaction between the growth rate of population and per capita income, how technological progress affects labor specialization, and the discovery of production methods and goods.

Smith's model of economic growth can be given by:
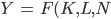
Where K is capital, L is labor, N is land, Y is output, and F is the production function.
He gave an analysis of markets working on a self-correction mechanism. By which he focused on the impulses of the acquisitive drive where the nation's wealth annual flow could be observed growing steadily.
The theory explained the rise in labor productivity with the help of the division of labor and capital accumulation.
2. Malthusian theory
It was proposed by Thomas Malthus. The theory suggested large population growth was caused by technological progress. Also, in the long run, no impact of technological progress was seen on per capita income.
Though technologically advanced economies had higher population densities, their per capita level of income did not differ from the technologically backward economies.
3. Classical growth theory
In this theory of growth, it is proposed that the theory of economic growth and production is based on the law of variable proportion.
The basic theme deals with development from the progressive state into a stationary state of an economy. A progressive state implies a high level of accumulation.
Accumulation permits an increase in output in an economy by the addition of productive resources, mainly those which help in raising labor productivity. This accumulation depends on the level of profits of the economy.
The theory suggests that in the short-run, wages( actual or market) are above subsistence level leading to an increase in population. As the population increases, wages approach subsistence levels in the long run.
The big push model, originated by Paul Rosenstein- Rodan, emphasized that the decision taken by the firm to industrialize or not is dependent on its expectation about what the other firms will do.
The model focused on underdeveloped countries. It is said that large amounts of investments are required to bring underdeveloped countries on the path of economic development.
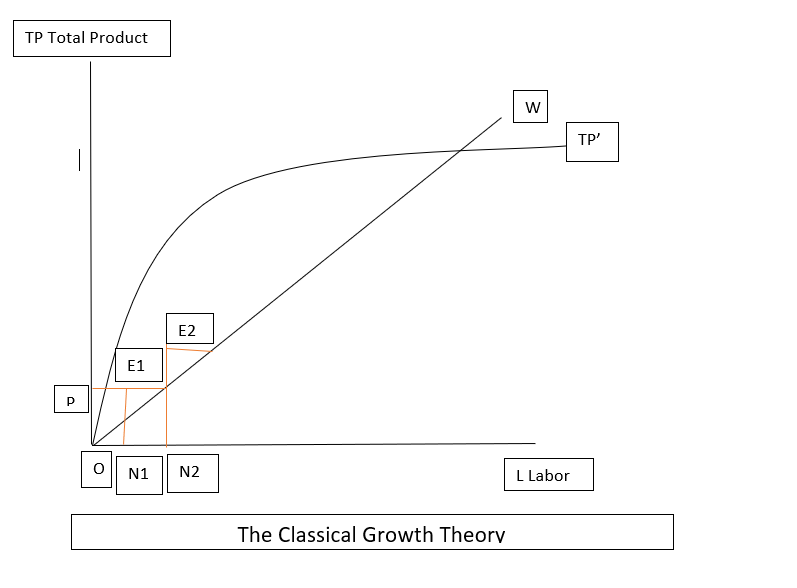
4. Solow- Swan model
The model was developed by Robert Solow and Trevor Swan. The model assumes diminishing returns to labor and capital. Capital in an economy is accumulated through investments.
A steady-state condition means that due to the diminishing returns to capital and lack of technological progress, an increase in capital per labor leads to economic output.
The output is reached where economic output and capital per labor stay constant as annual investment equals annual depreciation in the capital.
Growth in the model can be seen with technological progress or an increase in the share of an economy's gross domestic product (GDP). The model suggests that the economies that invest a large share of GDP for a long time are rich.
This model is an exogenous growth model as it does not provide an explanation of why the different share of GDP is invested by the economies and why the technology is improving over time.
Though the model accounts for an exogenous rate of investment, it implicitly, under certain conditions, predicts convergence in the rate of investment. This concept had conceptual flaws and was rarely achieved in practice.
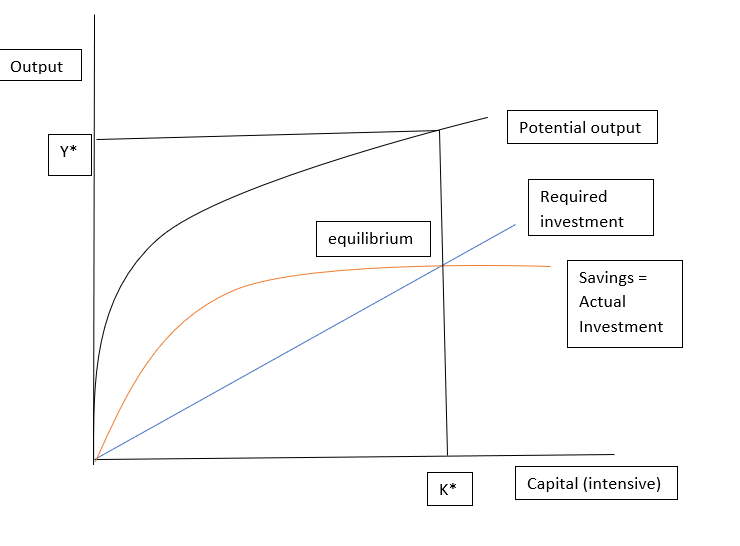
5. Endogenous growth theory
This theory was advanced by Robert Lucas, Jr. and Paul Romer in the 1980s. A new concept of human capital was incorporated by them, which gave an increasing rate of return.
Apart from human capital, innovation and knowledge were introduced as significant contributors to economic growth.
Concepts like positive externalities and spillover effects were seen leading toward economic growth.
The theory mainly holds for the long run and emphasizes that the long-run growth rate is dependent on policy measures.
Principles on which this theory relies are:
Government plays a vital role in raising the growth rate of a country to facilitate intense competition by stimulating production and innovation processes.
Increasing returns to scale are observed from human and other capital investments.
Technological progress is a result of the private sector's investment in research and development.
As a source of encouragement for businesses to engage in research and development, the protection of property rights and patents was important.
Growth requires investment in human capital.
For the creation and stimulation of new jobs, innovations, and investments, government policy should motivate entrepreneurship.
Romer said that technological change is not an exogenous by-product, as suggested by Solow.
He tried to prove that government policies are helpful for fostering endogenous innovation and economic growth.
6. Unified growth theory
It was proposed by Oded Galor and focused completely on the regime of modern growth, due to which it was unable to explain inequality across nations from the roots.

It suggested that the standard of living was near subsistence level across all spaces and time as population growth offset technological progress.
The theory of unified growth claims that the pace of technological progress can be increased with the help of enhancing education as education enables easy adaptation to change technological environments.
Fertility decline was triggered by the allocation of educational resources, which further led to a steady increase in per capita income, making way for sustained economic growth.
A transition from stagnation to growth was a result of cultural and institutional characteristics assuming ceteris paribus. This theory together captured fundamental phases of the development process in a single frame.
The fundamentals covered were:
Malthusian epoch and escape from the Malthusian trap
Human capital's emergence for growth
Fertility decline
Concept of the sustained economic growth process
Divulge roots of divergence in income per capita.
Everything You Need To Master Excel Modeling
To Help You Thrive in the Most Prestigious Jobs on Wall Street.
Researched and authored by Parul Gupta | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:


or Want to Sign up with your social account?