
Operating Margin
It measures the efficiency of a company's operations and profitability.
The operating margin (OM) is one of the many financial metrics for analyzing financial statements. This particular one measures the efficiency of a company's operations and profitability.

It is also known as the return on sales or EBIT margin and is calculated by determining the revenue a company gets to keep after accounting for operating expenses.
The formula for calculating OM is:
Operating margin = (Operating Income / Revenue (Net Sales)) *100
Fundamentally, the metric considers all the operating expenses a company incurs, for example, salaries and benefits. Yield to a more comprehensive metric than the gross margin.
| Revenue | $1,000,000 |
|---|---|
| COGS | $500,000 |
| Gross Profit | $500,000 |
| Operating expenses | $300,000 |
| Operating income | $200,000 |
| Operating margin | 20% |
In the example above, you can see a breakdown of company XYZ's finances. XYZ generated a gross profit of $500,000, i.e., Gross profit = revenue ($1,000,000) - COGS ($500,000).
When you subtract the operating expenses ($300,000), the operating income is left to be $200,000.
This is where the OM comes in. To calculate the return on sales, you divide the operating income by the revenue/sales that XYZ earned.
To beautify the result to a cleaner and easy-to-read figure, you multiply the result: in this case, 0.20 by 100.
Operating Margin = (200,000 / 1,000,000) *100
In this case, the margin for XYZ is 20%. This tells you that for every dollar of revenue XYZ generates, XYZ company keeps 20 cents in operating profit after deducting all the operating expenses.
NOTE
The operating income is a business's revenue after subtracting operating expenses such as salaries, rent, and utilities.
Overall, the margin provides a great preliminary insight into a company's efficiency and profitability.
It makes an important financial metric for investors, stakeholders, and management to look at and examine.
Importance of Operating Margin
The importance lies in its ability to show how efficiently a business uses its operational resources to generate profit.

A higher return on sales indicates that a business is keeping a higher revenue after paying off the operating expenses, which translates into higher profits.
Conversely, a low margin suggests the company spends too much on its operational expenses. As a result, it can eat into its profits.
One of the reasons companies may have a lower operating margin is because they are investing in R&D. So, in the short-term, their margins are lower in the hopes of new products and services that can generate more revenue.
Businesses can improve this margin in several ways. One approach is to reduce operating expenses while increasing their revenue, or at least maintaining it.
Moreover, this can be accomplished through cost-cutting measures: such as streamlining processes or negotiating better supplier contracts.
NOTE
Increasing revenue while maintaining or reducing operating expenses is another approach. This can be achieved by expanding into new markets or product lines or improving marketing and sales efforts to increase customer acquisition and retention.
A higher margin indicates that the business will likely have an effective pricing strategy and better control of its costs. Also, it can suggest that the company has a more efficient business model.
Analyzing this margin over time can reveal company financial performance trends. In addition, such analysis can inform management decisions on investments, cost-cutting, and other strategic initiatives.
Investors and creditors look up at a higher margin with bright eyes. It creates value for the shareholders and provides security for lenders to maintain their lending activities or extend new loans.
Example
Here is an example of a quarterly statement for Apple Inc.:
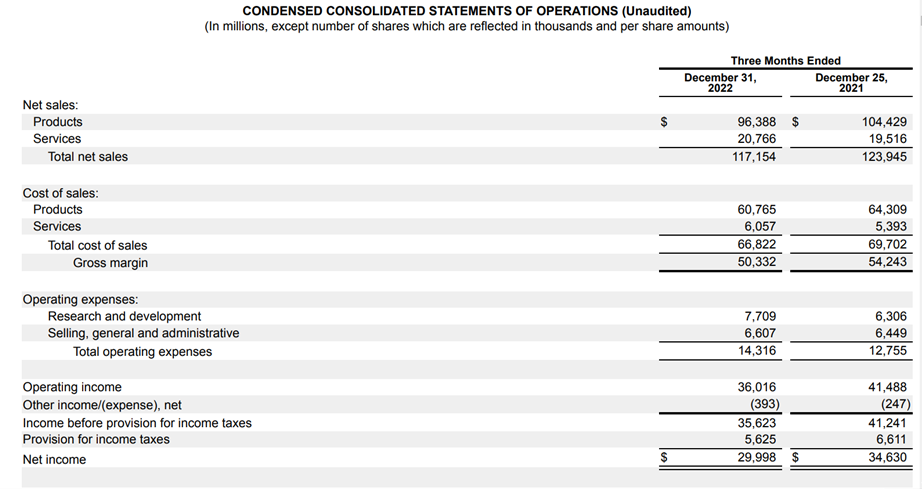
In this financial statement, we will focus on the current statement period, that is, the period ending on December 31, 2022. Please note that the figures for this statement are in millions.
Breaking down the statement, you can see that Apple generated net sales of $117,154; now, you can subtract $66,822, the total cost of sales (COGS). This gives you a gross margin of $50,332.
Going further down the statement, you reach the section on operating expenses. In the case of Apple, they reported expenses for research, development, selling, general, and administrative.
Adding those two figures, you get that Apple had total operating expenses of $14,316. Finally, you subtract the operating expenses ($14,316) from the gross margin ($50,332), resulting in an operating income of $36,016.
You have obtained the two figures to calculate Apple's operating margin.
Here is the formula to calculate the margin:
Operating margin = (Operating Income / Revenue (Net Sales)) *100
OM = (36,016 / 1117,154) *100 = 30.75%
So, for this 10Q, Apple's OM was 30.75%.
Drawbacks of Operating Margin
The return on sales has limitations. Primordially, it should be used to compare companies in the same industry or sector. Why?
Not all companies operate in the same ways and have the same business models or yearly sales. Comparing company A's sales return in the technology sector will be difficult compared to company B's in the retail industry.

Both companies operate in different ways and with different margins. Calculating and comparing their return in sales would therefore be meaningful. Comparing companies in the same sector with a high correlation between their business models and sales is better.
Additionally, the return on sales does not consider certain variables that may impact cash flow. They include working capital, capital expenditures, and non-operating expenses such as interests, taxes, and depreciation.
These variables, either included or excluded, can ultimately alter the cash flows, the capital coming in and out of business, to be higher or lower than the return on sales. Understanding a company's cash flow performance is essential to evaluate its financial health.
Cash flow encompasses the cash from revenue, investments, and other cash-in-flowing activities. Also, it registers the cash the company spends on expenses like salaries, R&D, inventory, etc.
Think about it as if it was your bank account. For instance, your account shows the money that comes in and out of it, and at the end of the month, you get a monthly statement showing you every transaction and ending balance.
NOTE
A positive cash flow signals that a company generates more cash than it is spending. The company can meet its obligations, invest in new projects, and exploit market opportunities.
EBIT Margin vs. Operating Margin
You might hear these two terms thrown out as synonyms. While correct, the primary difference between them is that EBIT includes all non-operating income, non-operating expenses, and other income, whereas the operating margin does not.

In a sense, everything being equal, operating income is also known as EBIT. Now if the income statement has a section that includes additional non-operating income and expenses, then that figure would change.
Operating and EBIT margins are colloquially intertwined because they exclude interest and taxes.
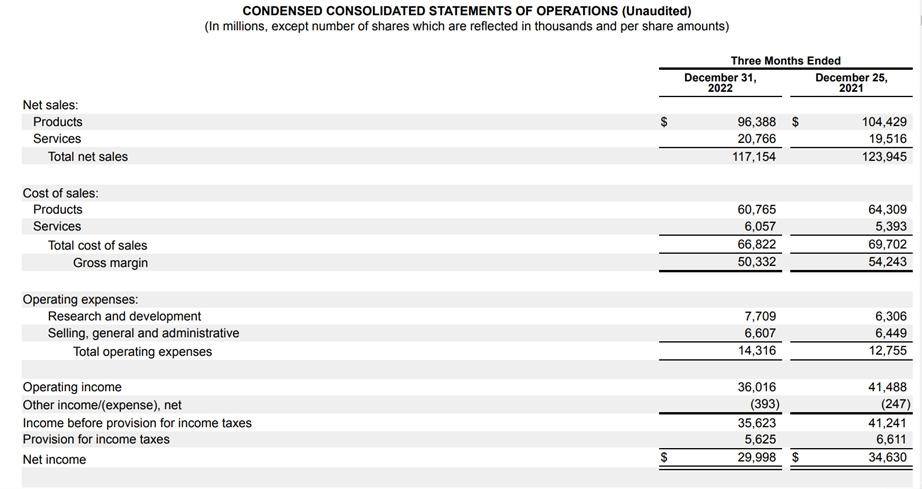
In our previous example, we found that the operating margin of Apple was 30.75%. Still, if you look closely at the quarterly income statement underneath the operating income of $36,016, there is an extra section called "other income/(expense), net."
That amounts to -$393, so you can add that operating income. In this case, you get that EBIT for Apple is $35,623, which makes the EBIT margin (EBIT / Revenue) 30.41%.
NOTE
EBIT is a non-GAAP (not Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) measure metric. However, operating income is a financial metric recognized and reported under GAAP. However, companies, analysts, and investors widely use EBIT alongside EBITDA.
Other Profitability Metrics
You can grasp a company's financial health over different levels of the income statement through the following metrics:

1. Gross margin
At the early levels, you can calculate the gross margin. It is a representation of the percentage that the company generates versus COGS.
The formula for the gross margin is:
Gross Margin = (Revenue - COGS) / Revenue
A higher gross margin signals that the business can manage costs and generate higher revenue.
2. Net Margin
You can find the net income near the end of the income statement. This is the total capital the business generates and includes all transactions for the reporting period, such as income received and expenses paid.
With the net income, you can calculate the net margin. The formula is:
Net Margin = Net Income / Sales
The net margin represents the percentage of profit a business keeps after accounting for all costs incurred. Therefore, a higher net margin indicates the company holds a higher rate per dollar.
Key Takeaways
- Operating margin measures a company's operational efficiency and profitability.
- It is calculated by dividing the operating income by the total revenue.
- Higher margins indicate better operational efficiency and profitability.
- Analyzing OM over time can reveal company financial performance trends and inform management decisions.
- This margin should be used to compare companies in the same industry or sector.

Everything You Need To Build Your Accounting Skills
To Help You Thrive in the Most Flexible Job in the World.
.jpg?itok=DxumzaOP)

or Want to Sign up with your social account?