
Tangible Assets
These are the value-holding assets of a company that are physical in nature
The word "tangible" describes anything that is perceptible by touch. Tangible assets, also known as fixed assets, are the value-holding assets of a company that are physical in nature. These assets include properties of a business, vehicles, cash, inventory, plant and equipment, and investments.

A word opposite to the above is intangible. These assets are the value-holding assets of a company that are not physical in nature. Intangible assets include accounts receivables, pre-payments, patents, copyrights, and goodwill.
Similar to these assets, there are tangible and intangible liabilities, which do not exist in physical form and exist in physical form, respectively. A few examples of current liabilities are accounts payables, bills, taxes, and employee payables.
All non-monetary commitments associated with stakeholders that the corporation must fulfill in order to avoid the depreciation of its intangible assets are referred to as intangible liabilities.
GAAP stands for "Generally Accepted Accounting Principles." These are a set of rules set up for accounting and financial reporting. Financial statements are also produced according to the rules and regulations set by GAAP.
Net tangible assets are all assets that are physical in nature and have a monetary value. It can be formulated as taking away net intangible assets and all liabilities from total assets.
The formula is listed as follows:
Tangible Assets = Total Assets - Net intangible assets - Total Liabilities
Where can you find tangible assets?
A balance sheet or statement of financial position is a document provided to the company's stakeholders, such as - investors, creditors, etc. document shows the financial position of a company; this includes critical information about the company such as - assets, liabilities, equity, etc.
The formula for the balance sheet is as follows:
Shareholder's Equity = Assets - Liabilities
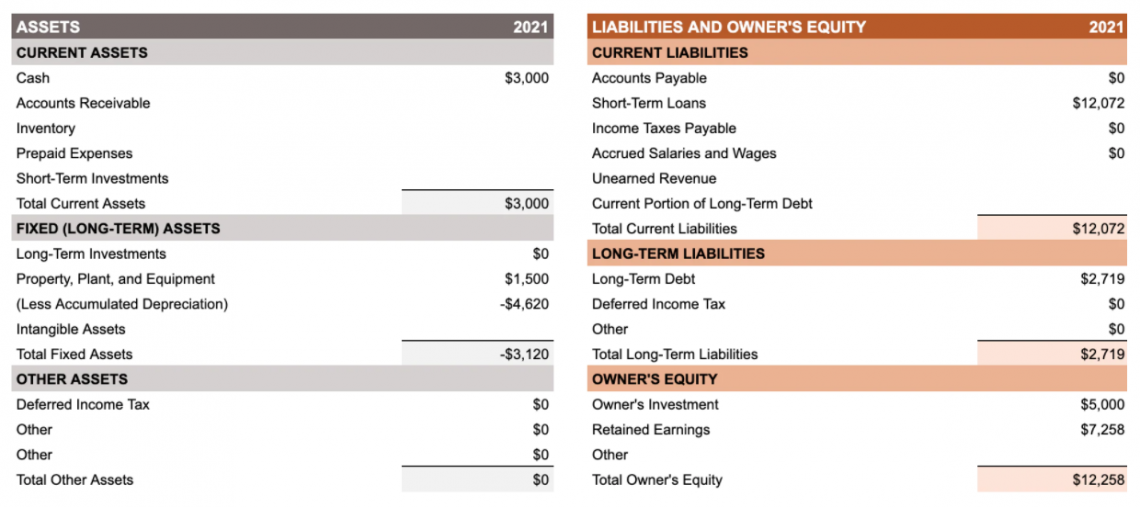
Financial statements of a company, such as - balance sheet, income statement, etc., can be used to assess the liquidity and efficiency of a business along with the rate of return it is providing to its shareholders.
As observed from the above figure, we can clearly see net tangible assets, also known as total fixed assets, under the category of assets. Assets are further divided into current assets and other assets. However, we will be discussing tangible assets.
Similar to the balance sheet, another important financial statement is the income statement, which is used by firms to analyze their financial performance.
Microsoft Excel is one of the most commonly used applications to prepare financial statements for a company. This is because it offers various features to assist users in creating or editing financial data.
WallStreet Oasis provides its users with financial modeling courses in Microsoft Excel.
Everything You Need To Master Excel Modeling
To Help You Thrive in the Most Prestigious Jobs on Wall Street.
Ratio Analysis
One of the most popular ratios which involve the calculation of tangible or fixed assets is the fixed asset turnover ratio, also termed as FAT. The efficiency with which a corporation generates net sales from its fixed-asset investments is measured by the fixed asset turnover ratio.

This ratio is used by the investors and creditors to know how efficiently management is using its fixed assets like machines, plants, equipment, etc. The fixed asset turnover ratio is an efficiency ratio and can be formulated as dividing total revenue by the value of fixed assets.
The formula is as follows:
Fixed Asset Turnover=Revenue/ Fixed assets
Fixed Asset Turnover=Net Sales/ Average Fixed Assets
There are certain values that are considered good from the point of view of investors and creditors. Any business with a FAT value greater than 1 is considered good, meaning the business is able to generate good revenue by efficiently using its fixed assets.
For example, if a company has a fixed asset turnover of 1.6, this means the company is generating $1.60 of sales for every dollar of assets the firm has.
A FAT value lower than 1 is considered as the management not using its fixed assets efficiently; therefore, it is not worth investing in. For example, if a company has a fixed asset turnover of 0.2, this means the company is not using its resources and fixed assets efficiently.
Difference between tangible and intangible assets
Intangible assets have a monetary worth since they represent potential earnings. A copyright on a song is an example of an intangible asset. The record company that owns the copyright would get paid a royalty each time the song is played.
| Basis | Tangible Assets | Intangible Assets |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The value holding assets of a company that are physical in nature. | The value holding assets of a company that are not physical in nature. |
| Depreciation & Amortization | They are subject to depreciation. | They are subject to amortization. |
| Residual value | Possess a residual value. | Have no residual value. |
| Disadvantage | They can be destroyed by natural calamities. | They can be lost due to poor decision-making. |
| Valuation | The value of these can be easily determined. | Valuation is harder in comparison to tangible assets. |
| Liquidity | Much easier to cash out due to their physical nature. | Are not easy to liquidate as they are not physical in nature. |
| Financial statements | Found under assets in the balance sheet. | Found in the balance sheet. |
| Examples | vehicles, cash, inventory, plants, equipment, and investments. | Accounts receivables, pre-payments, patents, copyrights, and goodwill. |
Uses and types
As understood from the above paragraphs, we know that these are physical in nature and possess money value in them.
These assets are used to supply a service or product, contribute to the financial flow of a company, raise funds in the event of an emergency, and in order to achieve your company's aims and ambitions.

Companies also use tangible assets as collateral for getting loans from banks. These are further divided into current and long-term tangible assets as explained below:
Current- These assets are ones that can be quickly converted into cash. This will be reported as revenue in an earnings report. A current asset is something like company inventory.
Long-term- Fixed assets, often known as long-term assets, are assets that will not be converted into cash within a year. As a result, their worth will deteriorate over time, and their cost will be spread out across the years of use.
A good example of a long-term asset is machinery.
Because it can be difficult to swap tangible assets for cash, different types of these will be treated differently in accounting. Fixed assets, such as real estate have less market liquidity and are more difficult to sell.
Examples
Below are a few examples of non-current assets discussed below
Cash - Being the first line item on an organization's balance sheet, therefore, increases the debt and decreases the credit. It is positioned at the top of the current asset section as items are arranged in order of their liquidity. It is one of the most liquid assets used to purchase other assets easily.

Cash assets include treasury bills, market funds, commercial papers, and other assets which can be easily converted into cash. Another kind of asset is cash value assets; these consist of both market value and cash value.
Inventory - Inventory serves as a major part of the business as it includes stocks, etc. as well.
Inventory includes -
- Raw materials
- Component parts
- Work in progress
- Finished goods
- Packing & packaging
Inventory serves the following functions in a business: -
- Provide & maintain good service to its customers
- Smooth flow of goods through the production process
- Provide protection and assurance against uncertainty in supply or demand
- To obtain an efficient utilization of resources such as people and equipment.
Property, Plant & Equipment (PPE) - Physical or tangible assets, such as PPE, are long-term assets with a lifespan of more than a year. These include furniture, machinery, and equipment that help companies to function efficiently.
Oil businesses, auto manufacturers, and steel companies are examples of capital-intensive industries with a large quantity of fixed assets.

Depreciation is the process of dividing the cost of fixed assets and expensing them over their estimated useful life. Depreciation allows a business to avoid paying a large cash outlay in the year that an asset is purchased.
Plant & equipment also includes vehicles like trucks, cranes, etc. These play a vital role in establishing a strong supply chain. Any business must be able to obtain supplies, transport them to a production site, and distribute their finished products.
Key Takeaways
- Tangible assets, also known as fixed assets, are the value-holding assets of a company that are physical in nature. Examples - vehicles, cash, inventory, plants and equipment, investments, etc.
- Tangibles are further subdivided into current and long-term intangible assets based on their useful life and their liquidity.
- These assets are the value-holding assets of a company that are not physical in nature. Examples - accounts receivables, pre-payments, patents, copyrights, and goodwill.
- GAAP stands for generally accepted accounting principles; these are a set of rules set up for accounting and financial reporting.
- The most popular ratio which involves the calculation of tangible or fixed assets is the fixed asset turnover ratio, also termed as the FAT.
- The value-holding assets of a company that are physical in nature are called intangible assets, whereas assets that are not physical in nature are tangible assets.
- They are used to supply a service or product, to contribute to the financial flow of a company, to raise funds in the event of an emergency, and in order to achieve your company's aims and ambitions.

Everything You Need To Master Financial Statement Modeling
To Help You Thrive in the Most Prestigious Jobs on Wall Street.
Researched and authored by Abhinav Bhardwaj | LinkedIn
Free Resources
To continue learning and advancing your career, check out these additional helpful WSO resources:


or Want to Sign up with your social account?